3D printing (also known as additive manufacturing) is being increasingly applied in many different industries. Usually, 3D printers are conceived as a prototyping tool for designers and makers. However, with the development of technology, 3D printing shows more potential in the entire production process.
Footwear manufacturers (Like Adidas, Nike) are one of the first companies that adopt 3D printing in the production process. They are using additive manufacturing (AM) for prototyping, in particular. In some cases, 3D printing helps create molds for traditional production. In other cases, footwear parts are created using only 3D printers.
In this example, we will use the footwear industry to show how 3D printing is applied for production. The main trends driving 3D tech adoption in footwear are:
- Footwear Customization
- Rapid Prototyping
- Manufacturing Footwear
Footwear Customization

Ecco Innovation Lab showcasing an in-store setup for its custom insole service
A range of companies offers custom footwear services. Mobile apps are often included as a perk, allowing customers to easily access and share 3D models and additional data about their required footwear. Ecco offers such a comprehensive footwear customization service. The fitting session requires about 10 minutes of the costumer’s time and can be performed on-site. It follows three basic steps:
- 30 sec. real-time scan
- Data-driven analysis and 3D modeling
- In-store 3D printing of custom insoles
These custom shoes cost between $390-445. Keep in mind, as the application of 3D technology expands within the footwear industry, such 3D custom services are likely to differentiate themselves among affordable and higher-end markets.
Traditional Materials vs AM Filaments
There are specific properties necessary for quality insoles, like good viscoelasticity, durability, and temperature stability. Polyurethane (PU) has long been used to provide quality and affordable insoles. But non-thermoplastic PU and rubber are not compatible filaments for AM. That’s why AM is developing viable alternatives like Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) that can be printed with FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) 3D printers. One of the benefits of FFF printers is their ability to create microstructures to fine-tune the properties of products. Oftentimes, it’s the cell size and internal design that makes the product more comfortable, lighter, and flexible.


Raise3D’s FFF printers can produce layer heights as low as <0.005 mm or 5 microns and are compatible with an ever-growing number of filaments like PLA, ABS, PET, Nylon, TPU, and PC.
Rapid Prototyping
Footwear production lines depend on several tasks that aren’t easily automated. That’s why it might take a while before AM footwear factories can become a reality. However, prototyping with 3D printers has already established itself within the footwear industry, also aiding in the creation of molds for traditional methods.

A PU midsole is peeled from a steel mold
Three years ago, A Chinese footwear manufacturer started prototyping with a Vat Polymerization 3D printer. Before using 3D printing, it took the design team about 15 days to complete a prototype. 3D printing cut this down to 3-4 days. A midsole can now be completed within 8-10 hours and will cost them around $100 to print. Furthermore, since they’re completed on-site the entire design process has become more transparent and intuitive. It also reduces investment risks, since they now have the chance to test different iterations of a design before proceeding into product development.

3D printed prototype created on-site by the Raise3D’ design team for manufacturers with rubberlike TPU filament.
The direct benefits of switching to 3D printing were:
- 80% less time consuming
- 70% cost reduction
- In-house access to prototypes (rapid-prototyping capabilities)
Manufacturing Footwear

The 3D printed midsole for Adidas’ Futurecraft 4D
In the highly competitive footwear market, 3D printing can: adequately cater to individual needs, shorten revision cycle times, and provide on-demand production. Furthermore, there are no leftover materials in 3D printing, reinforcing the sustainability of the technology. For example, Adidas is pressing the envelope of sustainable production with its Ocean Plastics line by having midsoles printed out of recycled fishing nets.

3D printed midsole produced by Adidas using recycled PET filament
Traditional Materials vs AM Filaments
Adidas opted for a type of Vat Polymerization technology for their midsoles, which relies on a tunable photochemical process. In this process, a vat of resin is cured using UV light to create each part. Adidas produced over 11 million pairs of shoes that contain ocean plastics in 2019 and has vowed to use recycled materials for all their PET products by 2024.
Uppers
Major shoe companies, like Nike and Reebok, have started implementing 3D printing technologies for footwear uppers. FFF technology is used to produce an array of TPU upper materials. The printers melt the filament, and then extrude it through a nozzle (e.g. Raise3D printers have dual extruders for simultaneous mirrored printing). By having shoe uppers 3D printed and automatically sewn to each shoe, companies drastically trim time, materials, and expenses. The benefits of using FFF are:
- Rapid-fire prototyping
- Optimized performance
- Footwear innovation (no glue, lightweight, intricate designs)
Furthermore, 3D printing offers the right flexibility for rapid-fire prototyping. This means many iterations can be reviewed and optimized in a shorter timeframe. This provides for more intricate, higher quality materials, like Nike’s first high-performance 3D uppers (see below), made with TPU filament. This resulted in featherlight, intricately lined prints. TPU can easily be combined with other materials, and can also be heated up to bond with yarns, so the glue can be avoided in parts of the shoemaking process.

The whole shoe printing make by Raise3D with TPU filament and E2 printers
AM is Shaping the Future of Footwear
3D prototyping, customization, and production have established themselves within the footwear industry. AM is expected to expand further as advancements are made within 3D automation.
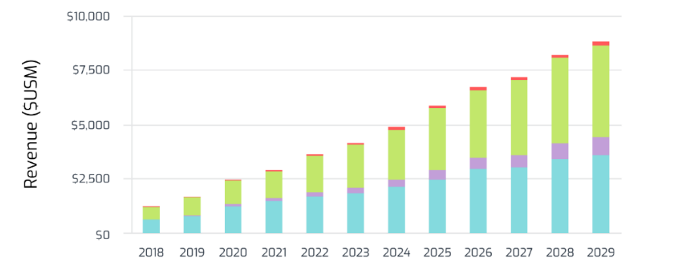
- In the upcoming decade, 3D printed footwear is projected to become the largest 3D printed consumer product, alongside household goods. 3D printing technology has experienced technological advancements and is now seen as a cost-effective manufacturing solution for mass production.
- The adoption of 3D technology within footwear is expected to grow year-over-year, accounting for over 8 billion dollars in revenue in 2029. The two main technologies profiting from this growth are FFF (in Blue) and Vat Polymerization (in Green).
- The macro trend of customization will continue to affect the footwear industry and will be accompanied by advances in 3D scanning and bio-mechanical sensor technology, as well as in intelligent learning and structural modeling.
- 3D production of shoe parts like midsoles and uppers will continue to grow. Currently, it accounts for about 35% of revenue. This is forecasted to expand to over 50% by 2029.
- Traditional prototyping will eventually be replaced by 3D prototyping within footwear design teams.
All in all, 3D printing is now making a huge impact on the footwear industry. It also shows great potential for many other industries. As more and more customers would like to choose customized products, 3D printing would bring more opportunities for all the traditional manufacturers.
Connect with Raise3D:
Have you had a great experience with Raise3D that you would like to share? Please contact us at inquiry@raise3d.com. We look forward to hearing from you.
For more information about Raise3D printers and services, browse our website, or schedule a demo with one of our 3D printing experts.









